Description
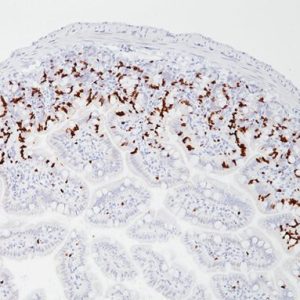
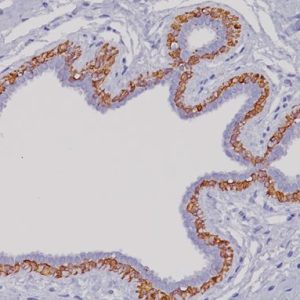
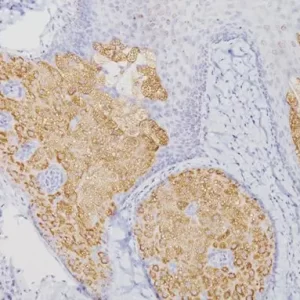
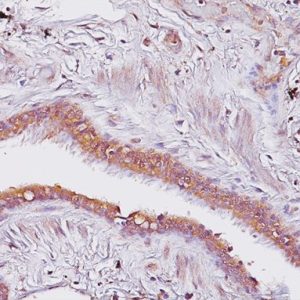
The oncogene-encoded protein c-Myc is postulated to play a role in activating the transcription of growth related genes. Amplification of the c-Myc gene has been found in several types of human tumors. Studies have shown that c-Myc is essential for vasculogenesis and angiogenesis in neoplastic disease. c-Myc oncogene activity may also be necessary for the translocation(s) seen in human breast tumors identified to have a poor-prognosis signature. Over-expression of the c-Myc oncogene has been implicated in the development and progression of human prostate carcinoma.
SPECIFICATIONS
Specifications
| WEIGHT | N/A |
|---|---|
| DIMENSIONS | N/A |
| INTENDED USE | IVD |
| SPECIES REACTIVITY | Human |
| SOURCE | Rabbit Monoclonal |
| CLONE | EP121 (previously known as Y69) |
| ISOTYPE | IgG |
| ANTIGEN | Synthetic peptide corresponding to residues in N-terminus of human c-Myc |
| LOCALIZATION | Nucleus |
| POSITIVE CONTROL | Some prostate or breast cancer |
DATASHEETS & SDS
INTERNATIONAL
REFERENCES
1. Wolfer A, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb; 107(8):3698-703.
2. Gurel B, et al. Mod Pathol. 2008 Sep; 21(9):1156-67.
3. Park K, et al. Hum Pathol. 2005 Jun; 36(6):634-9.
4. Yang G, et al. Cancer. 2005 Mar; 103(6):1186-94.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.